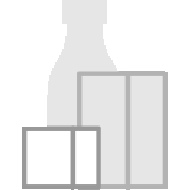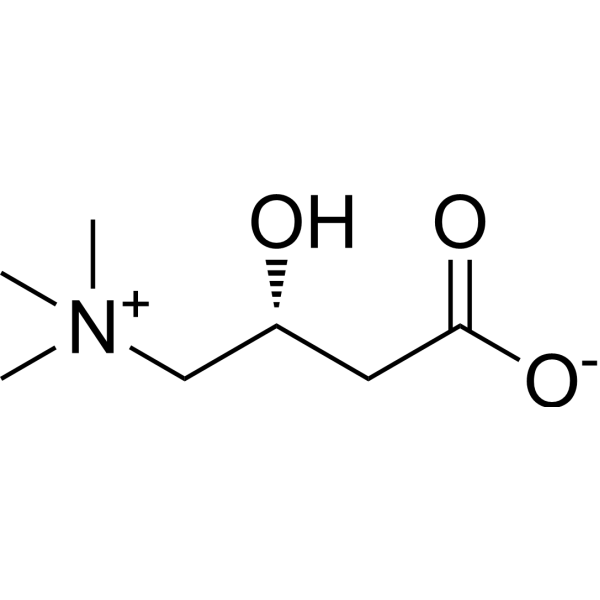
L-Carnitine ((R)-Carnitine), Co-factor for β-oxidation
L-Carnitine ((R)-Carnitine), a highly polar, small zwitterion, is an essential co-factor for the mitochondrial β-oxidation pathway. L-Carnitine functions to transport long chain fatty acyl-CoAs into the mitochondria for degradation by β-oxidation. L-Carnitine is an antioxidant. L-Carnitine can ameliorate metabolic imbalances in many inborn errors of metabolism. - Mechanism of Action & Protocol.

Dietary l-carnitine regulates liver lipid metabolism via simultaneously activating fatty acid β-oxidation and suppressing endoplasmic reticulum stress in large yellow croaker fed with high-fat diets, British Journal of Nutrition
fatty acid metabolism MedChemExpress (MCE) Life Science Reagents

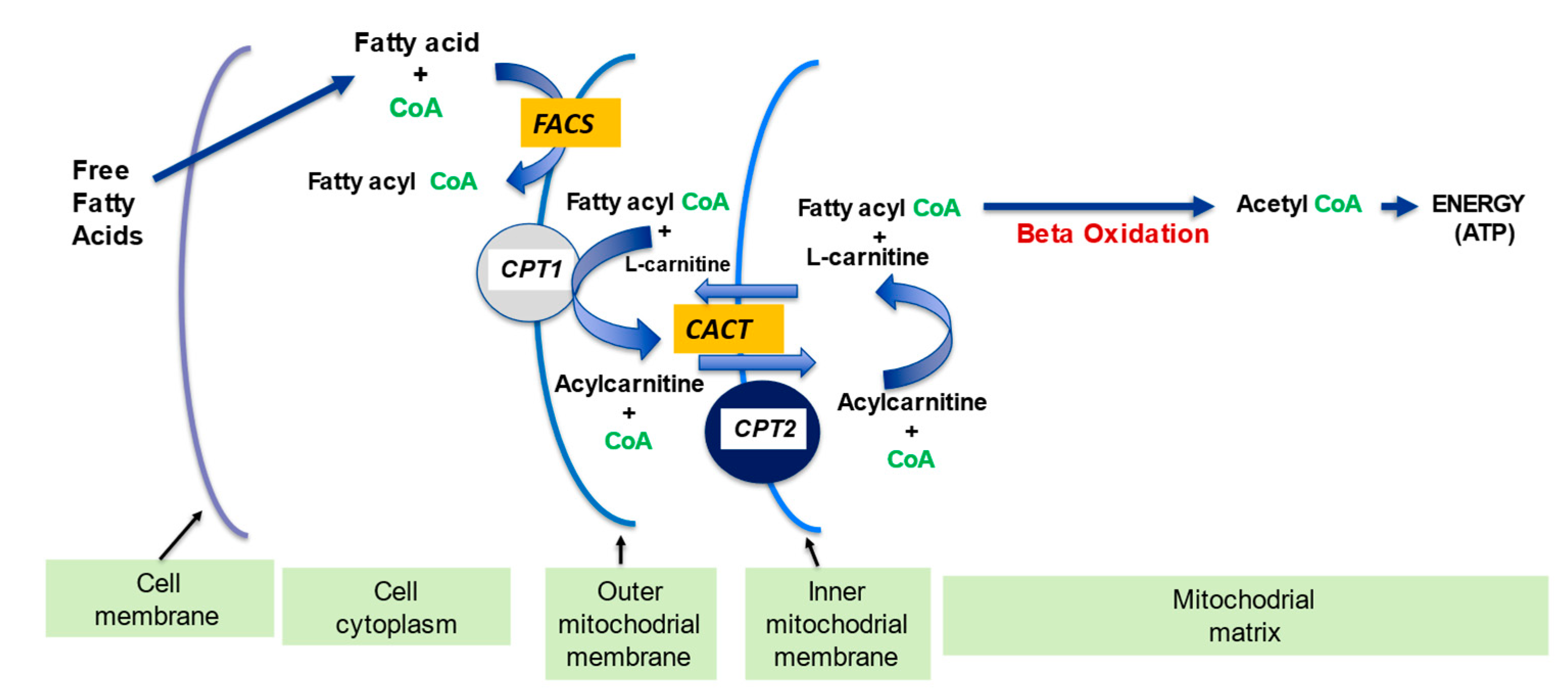
Role of L-carnitine in oxidative metabolism. CoASH, acetyl-CoA; CPT

PDF] Carnitine biosynthesis in mammals.

Enzymology of the carnitine biosynthesis pathway - Strijbis - 2010 - IUBMB Life - Wiley Online Library

Acetylcarnitine - Wikipedia
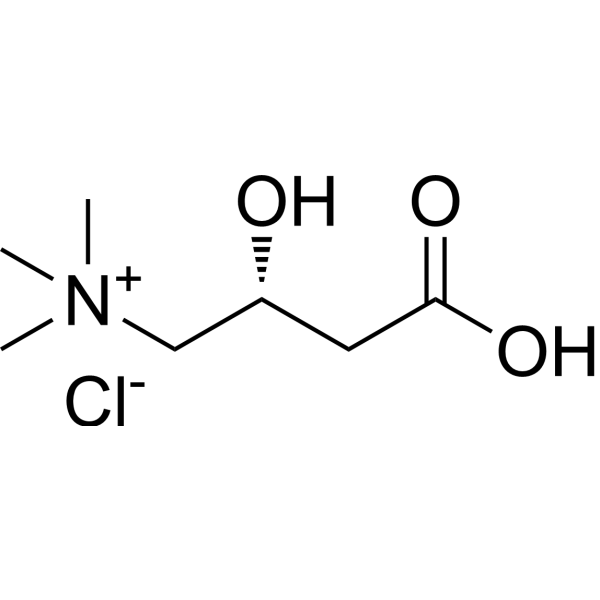
L-Carnitine hydrochloride ((R)-Carnitine hydrochloride), Co-factor for β- oxidation
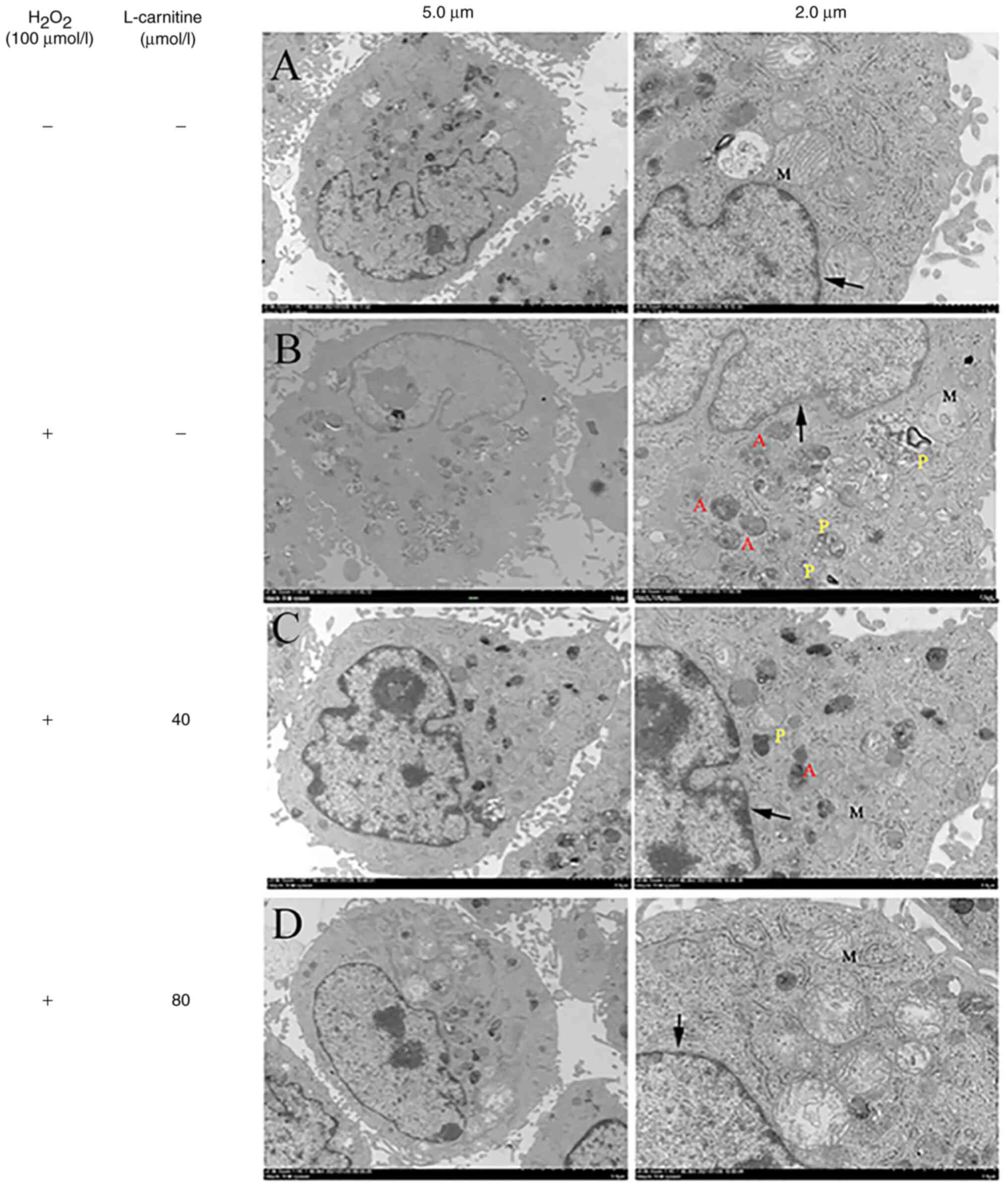
Protective effect of L‑carnitine against oxidative stress injury in human ovarian granulosa cells

Hyperpolarized [1-13C]Acetyl-l-Carnitine Probes Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle Activity In Vivo

Improving diagnosis of mitochondrial fatty-acid oxidation disorders
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Carnitine Complex – Naturally Nourished

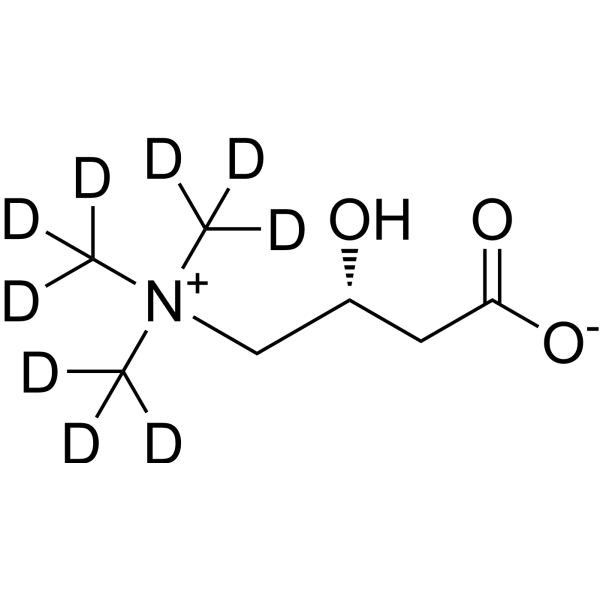
L-Carnitine-d3 (chloride) ((–)-Carnitine-d3, R-Carnitine-d3, Levocarnitine-d3, CAS Number: 350818-62-1)
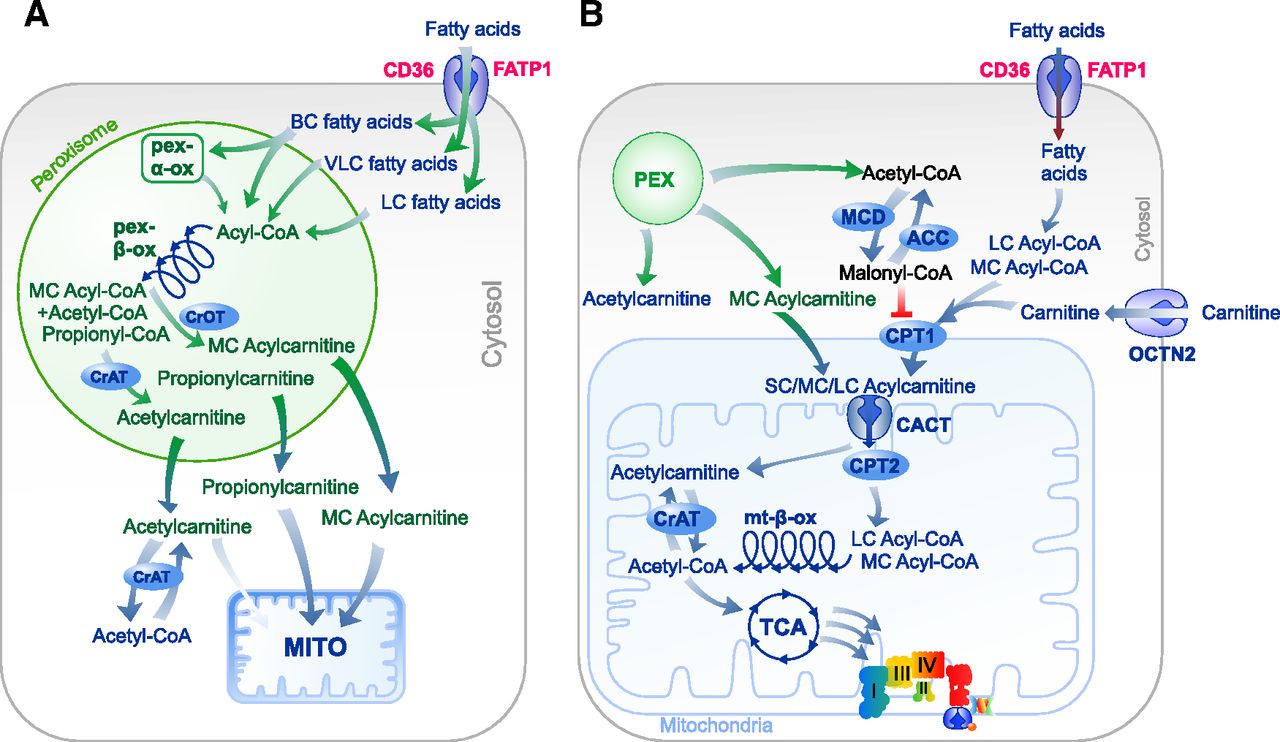
Acylcarnitines: Nomenclature, Biomarkers, Therapeutic Potential, Drug Targets, and Clinical Trials